BDB650
Classical PM
Stakeholder Management and Communications
Summary
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder Analysis
Communications Plan
Stakeholder Management
Who's a Stakeholder
Stakeholders are all of those who have an interest (stake) in the project
I.e., they will be affected in some way by it
As a result, they will have an interest in influencing it
Who's a Stakeholder
In data analytics, stakeholders can be:
→ The organization behind it
→ Clients (Customers)
→ Data Scientists working directly or indirectly on it
→ People who will use it
→ People affected by it
List of Stakeholders
Internal
→ Top management
→ Direct managers
→ Data Scientists
→ QA Specialists
External
→ Clients (customers, users)
→ Government (regulatory)
→ Contractors and suppliers
→ Anyone affected
Stakeholders over time
Stakeholder influence is often greatest at early stages
This normally drops during the middle stages...
... and increases again during the final stages
Note: Agile methods try to maintain engagement throuhgout the project
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholders Analysis
First, it is important to identify all stakeholders
Then, you need to classify them according to two dimensions:
→ Their level of power to influence the project
→ Their level of interest in the project
This classification can be captured in a stakeholder analysis matrix
Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
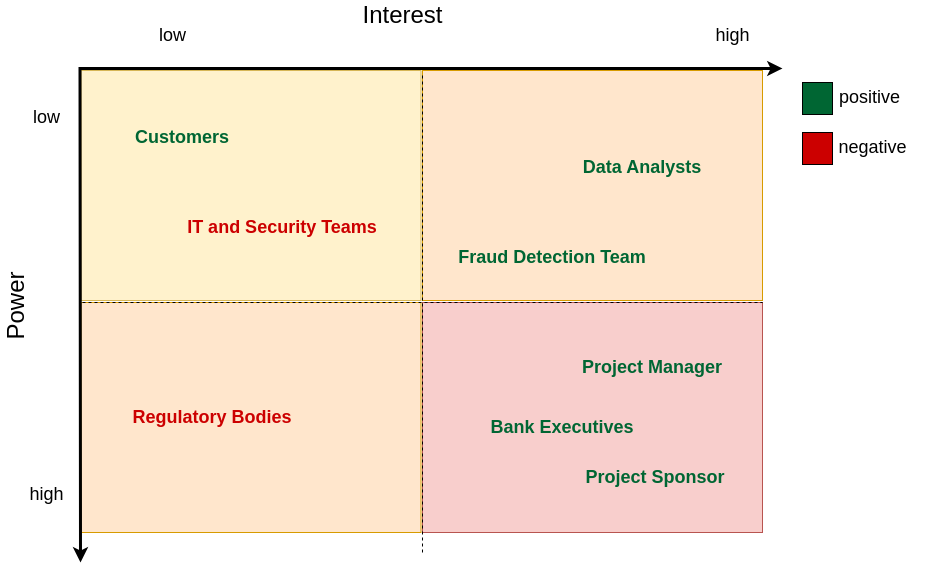
Stakeholder Analysis
After classification, you must develop stakeholder management strategies
Strategies are developed based on:
→ Their spot in the stakeholder analysis matrix (e.g. high-power and high-motivated)
→ Their attitude towards the project: positive or negative
Management Strategies
High Power and High Interest
Positive Attitude:
→ Keep them informed and involved
→ Meet often and consult about changes
→ Encourage their participation
Management Strategies
High Power and High Interest
Negative Attitude:
→ Attempt to gain their support and confidence
→ Find out what they need/want
→ Counter their negative influence on others
→ More strategies here
Communications Plan
Overview
A communication plan allows you to set expectations and standards
It defines how and when information is shared
It also defines what is shared and who receives the information
In Scrum, this is part of a Working Agreement
Comms Plan Format
Communication Plans are often written in tabular form
This makes the information more concise, structured, and easy to reference
What To Include
A list of items to be communicated with:
→ The person responsible (owner) for communicating the item
→ Names of all stakeholders involved (target audience)
→ A schedule or frequency of updates
→ The preferred communications channel
Things not to include
Project Plan Details
Confidential or sensitive details
Unclear or unrealistic expectations
Notes on Comms Plan
Your communications plan is deeply tied to your stakeholder analysis
It should address the stakeholder management strategies
For example, high power and high interest stakeholders should receive frequent communications
Example
| Information | Owner | Audience | Schedule | Channel | |----------|:-------------|:------| :-------| :-------| | Project Status | Project Manager | Bank Executives, Data Scientists | Biweekly | In Person | | Sprint Review | Data Scientists | Project Manager, Project Sponsor | Biweekly | In Person | | Modelling Results | Data Scientists | Fraud Detection, IT and Security Teams | Monthly | MS Teams | | Financial Report | Project Sponsor | Project Manager, Bank Executives | Monthly | Phone | | Compliance Reports | Project Manager| Regulatory Bodies | Quarterly | Email | | Advertisement | Project Sponsor| Customers | End of Project | Email |
Reading Material
Communications Plan (until "Improve team communication from start to finish...")